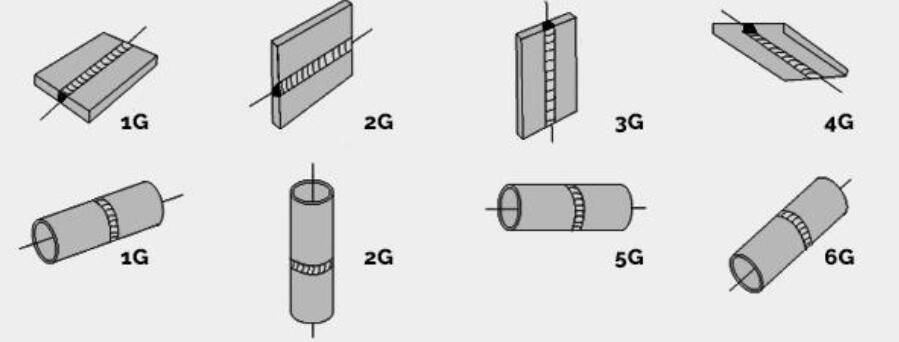
Each G level has specific technical requirements and application scenarios,
and welders need to undergo relevant training and certification to engage in these welding tasks.
1. **1G (Flat Position)**:
- The pipe is placed horizontally, and welding is performed on the outer surface of the pipe.
- Typically used for welding straight pipes.
2. **2G (Vertical Position)**:
- The pipe is placed vertically, and welding is performed on the outer surface of the pipe.
- Suitable for connecting vertical pipes.
3. **3G (Vertical Inside Welding)**:
- The pipe is placed vertically, and welding is performed on the inner surface of the pipe.
- Generally used for inner wall welding of vertical pipes.
4. **4G (Overhead Position)**:
- The pipe is positioned above the welder's head, and welding is performed on the upper side of the pipe.
- This welding position requires a higher level of skill.
5. **5G (Fixed Pipe Welding)**:
- The pipe is placed horizontally but cannot be rotated; welding is performed on the outer surface.
- Suitable for situations where welding must be done in a fixed position.
6. **6G (Inclined Position)**:
- The pipe is inclined at a 45-degree angle, and welding is performed in this position.
- This welding position has a high technical difficulty and requires the welder to have strong skills and experience.
All rights reserved by Hanzo Technologies Co., Ltd.